2024
Energy Storage Report
Key Trends and Drivers
Key Trends and Drivers in Energy Storage Capacity
The global energy storage industry is characterized by dynamic growth, fueled by various factors encompassing energy policy, technological advancements, and trade dynamics. This section provides an overview of some of the major trends and drivers shaping the industry on a global scale.
The increasing penetration of renewable energy globally, particularly in Europe, is driving the need for energy storage solutions.
Energy Transition and Renewable Energy Penetration
The increasing penetration of renewable energy globally, particularly in Europe, is driving the need for energy storage solutions. Just as Europe leads in renewable energy adoption, it also faces significant related challenges in grid management Energy Institute, 2023). Looking ahead at ambitious targets for renewable energy capacity expansion suggests integration challenges could intensify spurring the need for timely investments in energy storage capacities.
High renewable energy penetration markets face several challenges, including grid supply curtailment, power market price cannibalization, and negative prices. Grid unpreparedness often results in curtailment, where excess renewable energy production exceeds grid capacity. California, a leader in renewable energy adoption, saw a significant 60% year-on-year increase in grid curtailment in 2022 ( (AJOT, 2023). This oversupply depresses bulk power market prices, impacting project profitability, as fixed contracted prices are common. Additionally, grid curtailment leads to instances of negative prices, where operators cannot absorb excess energy and must compensate generators. The UK’s National Grid paid £215m to generators in 2022 due to unabsorbed energy (Power Technology, 2023).
Source: Source: Source: Energy Institute Statistical Review of World Energy
The rise of renewables also displaces conventional coal-based generation, accelerating the global phase-out of coal power. However, this poses challenges for grid operators, as coal plants provide baseload power crucial for grid stability. During the 2022 energy crisis, European countries faced coal plant postponements or reactivations due to restricted natural gas supply, highlighting the need for grid-scale storage and flexible energy sources.
Relative Share of Coal and Renewable in Global Power Generation
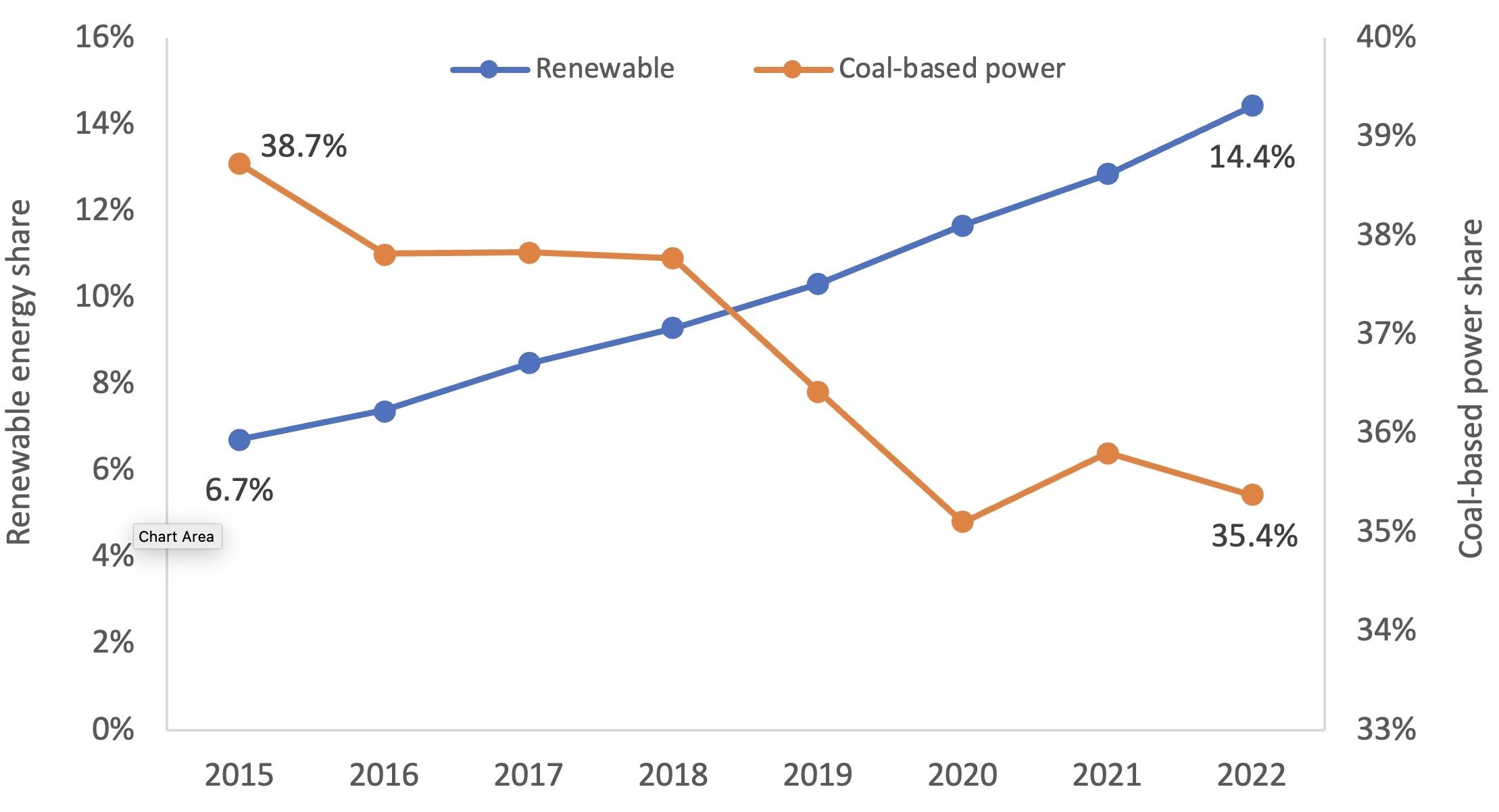
Note: Data refers to share of energy units generated by renewable and coal-based sources.
Role of Policy support
Renewable Energy Targets in the Major Markets/Regions
| Country/Regrion | Renewable energy target of 2030 |
|---|---|
| India | 40% zero-carbon generation by 2030 (including nuclear power) |
| China | 28% renewables by 2030 |
| United States | 739GW of wind and solar by 2030 to reach zero-carbon electricity by 2035 |
| United Kingdom | 60% renewables by 2030 |
| European Union | 42.5% renewables by 2030, under the REPowerEU |
Source: SNE Research
Elsewhere, many countries, including those in Europe and China, support battery storage projects through government-led auctions or subsidy programs. These are typically designed as technology-neutral power procurement contracts but largely attract hybrid and standalone storage projects. European energy storage auctions, such as Germany’s innovation tenders, allocate storage capacity through competitive bidding, encouraging hybrid and standalone storage projects. German authorities plan to award about 4GWh worth of storage contracts by 2028 (Fluence, 2023). Eastern European countries are also embracing battery storage, with plans to allocate grid connections to significant capacity and make regulatory changes to facilitate market participation. In Poland, there are plans to allocate grid connections to 9GW of battery storage projects, while another 16GW are registered for an ongoing market auction as of December 2023 (Energy Storage News, 2023). Hungary is in the process of implementing the first energy storage auction targeting 900MWh by 2026, and Estonia has announced energy-storage-specific grants pending the finalization of regulations.
China, the dominant country in battery production, implements subsidy programs to incentivize new energy storage capacities. In Xinjiang province, standalone battery storage units are entitled to compensation for discharged energy, with specific incentives for peak shaving and ancillary services. The standalone battery storage units were entitled to a compensation of CNY0.2/kWh (discharged energy) till 2025, with a 20% tapering off in each of 2024 and 2025. The subsidy scheme also outlined the incentives for specific services – peak shaving and ancillary services could qualify for CNY0.55/kWh in charging and CNY0.25/kWh in discharging without simultaneous capacity compensation (CESA, 2023).
Similarly, Chile is proactively promoting energy storage to complement its renewable energy generation base. In June 2023, the government’s energy authority announced preliminary bidding information to procure 5.4GWh split for contracted delivery in 2027 and 2028. In the same period, the government also announced an additional $5 billion worth of investment towards the energy storage systems ready for commissioning within 2026. Notably, most of the planned storage units are co-located batteries with utility-scale solar PV generation units in the famed Atacama Desert region. Chile’s latest policy announcements follow previous steps at facilitating market participation of the grid-scale storage units (Energy Storage News, 2023).
Overall, the policy-led funding approach is expected to gain traction in various markets as energy storage projects become increasingly important for achieving climate mitigation, decarbonization, and net-zero goals. As clean energy investments continue to grow globally, greater policy support and funding can be anticipated to accelerate the deployment of energy storage technologies.
Installed Capacity and Growth
Note: The data point for 2023 is an estimate based on BNEF’s expected new battery project build
Source: BNEF Energy Market Outlook
As the demand for energy storage continues to rise, so does the projected annual capacity addition. This growth will stem not only from an increase in the number of projects but also from larger-scale projects. In August 2023, Vistra Energy, a US-based retail power supply and generation company and a battery storage developer, announced the completion of Phase-III of its Moss Landing project, bringing its total capacity to 3,000MWh. This marked the project as the world’s largest, surpassing the 1,400MWh Californian battery storage project that held the title in 2022 Electrek, 2023) Energy Storage News, 2023). With enabling regulations and financing, more developers are likely to enter the market. In December 2023, Australia’s largest grid-scale battery, with a capacity of 1,000MWh, received final investment approval for construction commencement in 2024 ARENA, 2023).
Note: The capacity figure for 2023 is an estimated one using the average annual growth rates of 2021 and 2022
Source: IRENA, Alchemy Research
Major Pumped Hydro Storage Projects Under Planning or Development
| Project | Company | Particulars |
|---|---|---|
| Coire Glas | 1.5GW | UK’s first large-scale pumped storage project proposed in over 40 years. The final investment decision is expected in 2024. |
| Snowy 2.0 | 2.2GW | Australian government approved the AUD12 billion project’s revised development plans in December 2023. |
| Ebensee | 170MW | Austrian project, targeting 2027 for commissioning. |
| Red John | 450MW | Statkraft acquired this UK project from Intelligent Land Investments Group in December 2023. |
Source: Power Engineering International, PV Magazine, Statkraft company press release
Progressively, there is a strong preference for co-located battery storage installations, led mainly by solar PV and battery combinations. A weak grid integration in most markets makes co-located batteries attractive in managing grid scheduling. An added benefit is the lower capital outlay and land and grid infrastructure optimisation. The US market’s project pipeline for 2024 has a 70:30 split between co-located and standalone battery assets (Energy Storage News, 2024). Till 2022, co-location was incentivised with tax credits in the US market. The predominant share indicates that tax credits are not the only incentives for developers in this model.
The most common battery co-location projects are with solar PV. It is partly related to the relatively faster growth in utility-scale solar PV, among other renewable energy technologies. Battery storage co-located with a solar PV plant would enable grid services such as dynamic containment, besides mitigating the profitability risks that arise from excess supplies in the grid. Project pipelines in major battery storage markets, such as the US and UK, show a progressively rising interest in solar-plus-storage projects. The relatively higher investment returns in such projects potentially outweigh the complexities (such as separate permits, feasibility studies, etc.).
Some investment funds have also adopted the retrofitting route in battery colocation. In 2023, NextEnergy Solar Fund initiated retrofitting of battery storage to its solar PV portfolio for better returns. The declining subsidies in the renewable energy markets worldwide make co-located battery storage a better proposition for investors and developers seeking to maximise returns.
The drive for larger storage capacity sizes is closely linked to the demand for cost-competitive options and improved storage duration.
Emphasis on Utility-scale storage
Note: The above data is as of 2022
Source: IEA
Government-backed large-scale tenders play a pivotal role in this space. For instance, New York State aims to add 6GW of storage capacity by 2030 through centralized procurement addition (Utility Dive, 2023), while Australia’s Capacity Investment Scheme tender aims to expedite grid-scale storage capacity procurement (Construction World, 2023). In India, a planned $2.6 billion subsidy package aims to promote grid batteries (Mint, 2023). These tenders not only contribute to project pipeline capacity but also generate economies of scale, potentially leading to lower average costs.
Note: Data above is based on estimated/projected capacity addition of 2023
Source: McKinsey
The dominance of Lithium-Ion battery technology remains strong in the storage sector, supported by its maturity and economies of scale driving down costs over time.
Cost Economics
Note: Data for 2023 is as of November 2023
Source: BNEF Annual Battery Price Survey of 2023
However, battery prices vary widely across regions due to local market dynamics. China boasts lower average battery pack prices compared to the US and Europe, attributed to intense price competition and rapid manufacturing capacity expansion. Geopolitical factors, such as new US regulations targeting Chinese-origin battery components, introduce additional price distortions CNN, 2023).. Whilst the average battery pack price in China, as of 2023, was reported at $126/kWh, elsewhere in the US and European markets prices were 11% and 20% higher respectively.
Despite these challenges, battery storage units are increasingly competitive in the grid power mix, particularly in hybrid renewables plus storage projects Lazard, 2023). Many of these projects are now competitive against gas-based peaking power units, driven by revenue stacking opportunities from grid services and wholesale power market transactions.
Comparative view of Unsubsidised Levellised Costs across Fuel Mix vis-à-vis Batteries
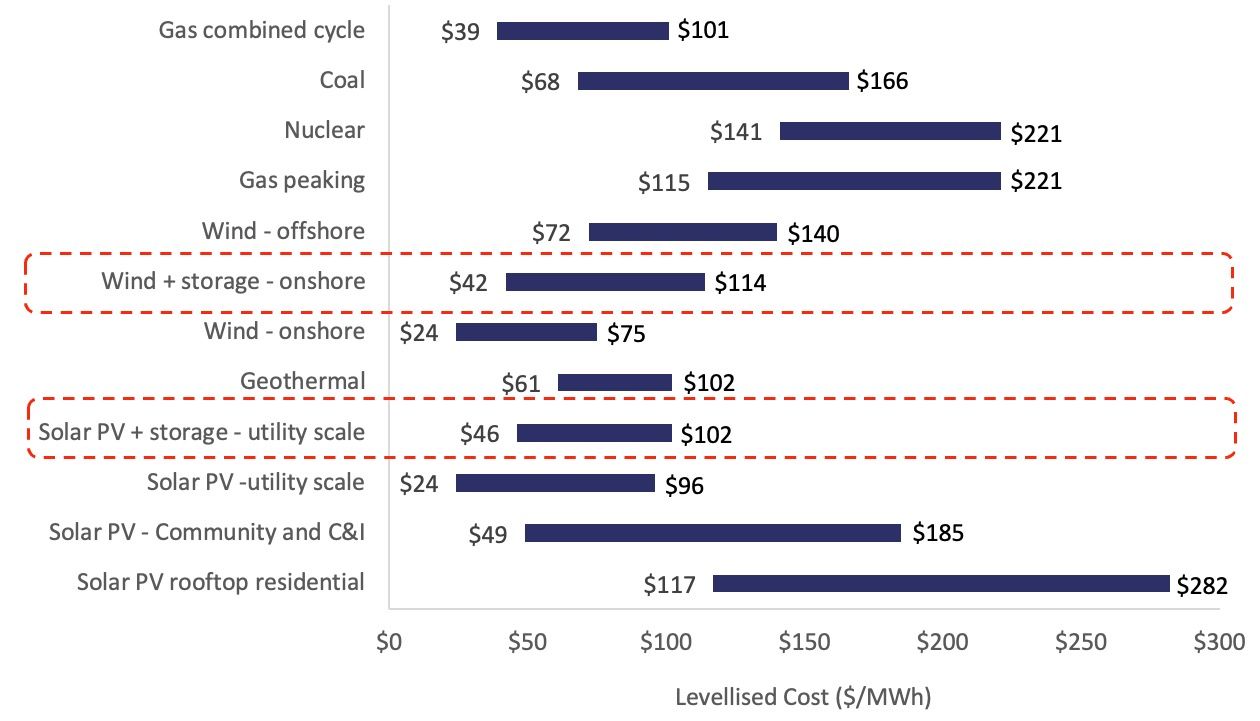
Note: Above data is illustrative, as of April 2023, and refers to the US market
Source: Lazard
The downward pressure on battery metal prices is anticipated to continue through 2024 and 2025 before any signs of recovery in the price trend emerge. Both demand and supply factors contribute to this outlook. On the demand side, a weaker electric vehicle market, driven by a slower Chinese economy, sluggish US market sales, and high interest rates, has dampened demand. This is significant as over 90% of battery demand comes from electric vehicles. Concurrently, miners have expanded the supply of critical minerals in anticipation of future demand. This expansion includes major battery metals such as Lithium, Cobalt, and Nickel. The pricing pressure is expected to persist due to the influx of additional supplies into the market as leading producers have expanded capacities in anticipation of future demand, despite the long lead times involved.
Lithium Supply and Price Outlook
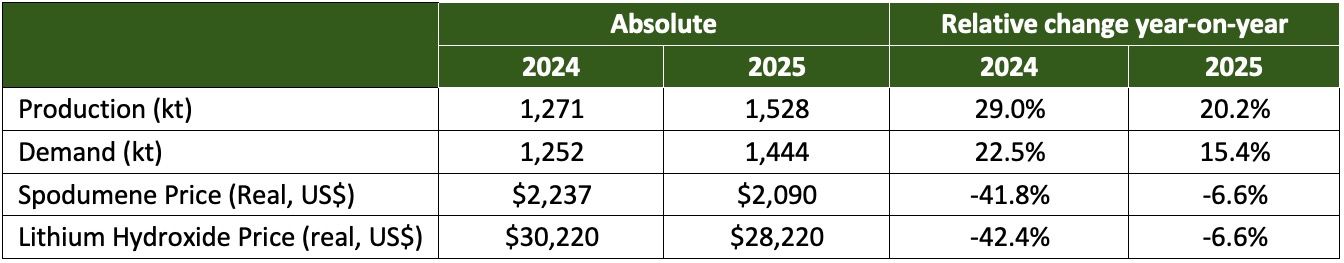
Source: Australian Government Department of Industry, Science and Resources
Lower raw material prices are expected to alleviate the cost pressures on battery storage developers, particularly as they prepare for capacity auctions by regulators and grid operators. According to the BNEF battery survey of 2023, the projected average battery pack price for 2024 is $133/kWh (BNEF, 2023). BNEF’s estimates further suggest that average battery pack prices could decrease to $113/kWh in 2025 and continue to decline, reaching below $100 by 2030 Energy Storage News, 2023). As of December 2023, BNEF’s tracked benchmark LCOE for four-hour battery storage reached its lowest point in decades, being 22% lower than the peak in 2022 BNEF, 2023).
Crucially, the reduction in battery pack costs resulting from lower battery metal prices has been able to counterbalance the impact of higher financing costs in recent years. However, high interest rates remain a significant factor. There are expectations of a potential easing in 2024, with the US central bank’s benchmark rates possibly peaking during the year before a potential reduction. Nonetheless, high interest rates are just one element in a mix of factors—including supply chain uncertainty, foreign trade restrictions, and regulatory developments—that collectively contribute to costs exceeding estimated ranges. It’s worth noting that as of Q1 2023, over three-quarters of US-based clean energy projects, including storage projects, face delays in their planned commissioning within or before 2025 due to a combination of cost factors Utility Dive, 2023).
Revenue Streams
Battery storage projects typically adopt a revenue-stacking strategy, which involves leveraging multiple revenue streams simultaneously. These revenue streams commonly include arbitrage, ancillary services, and participation in capacity auctions.
The revenue-stacking approach allows projects to diversify their income sources, reducing reliance on any single revenue stream and enhancing overall profitability. By tapping into various revenue streams, battery storage projects can optimize their financial performance and mitigate risks associated with fluctuations in market conditions or regulatory changes.
Moreover, the scope of revenue stacking is a critical consideration in the financing decision-making process for battery storage projects. Investors and financiers assess the potential revenue streams available to a project and evaluate their stability and growth prospects. Projects with robust revenue-stacking opportunities are generally viewed more favorably by investors, as they offer greater financial resilience and potential for attractive returns on investment.
The revenue opportunities for battery storage projects vary across different local power markets, depending on their stage of development and maturity. Here are some notable illustrations:
| Country/Region | Battery Storage Revenue Drivers |
|---|---|
Germany | The utility-scale battery storage market in Germany is growing rapidly, offering opportunities for new entrants. Ancillary and trading markets are promising revenue segments, with potential growth in day-ahead and intraday optimization. Regulatory measures, such as the introduction of a new capacity mechanism, could enhance revenue certainty for developers (Ion Analytics, 2024), (Timera Energy, 2023) |
Italy | Italy’s utility-scale battery storage market is nascent, with policy and regulatory measures incentivizing investments. Battery storage systems were allowed to participate in the wholesale and ancillary services segment in July 2023. A structural reform of dispatch procurement after 2025 may introduce new market-based services for battery storage units. Capacity markets offer 15-year contracts for new capacities, and regulators have proposed an auction-based scheme for procurement (Aurora, 2023) |
United States | The ERCOT Contingency Reserve Service (ECRS), introduced in June 2023, addresses frequency recovery during generation loss and provides capacity during net load uncertainty. Despite running only 21 days in H1 2023, ECRS contributed 15% of battery storage revenues (Modo Energy, 2023)
|
United Kingdom | Frequency response services were previously dominant revenue sources for battery storage units but have become saturated due to rapid capacity addition. Balancing Mechanism and Arbitrage have emerged as primary revenue sources, with the grid operator projecting GBP2 billion spending on grid balancing by the end of 2024. Capacity markets also play a crucial role in providing guaranteed contracted payments (PV Magazine, 2024), (Energy Storage News, 2024)
|