2023
Gigafactory Report
Gigafactory Pipeline
03 | Gigafactory Pipeline
03 | Gigafactory Pipeline
Introduction
Introduction
Based on the information available through April 2023, it is anticipated that the Gigafactory battery manufacturing sector will see an aggregate commissioned capacity exceeding 6 terawatt-hours (TWh). This substantial growth in manufacturing capacity can be attributed to the surging demand for electric vehicles (EVs). Furthermore, it is expected that additional projects will be announced as the Gigafactory pipeline continues to evolve, potentially driven by increased demand from various industries.
Nevertheless, it is important to acknowledge the prevailing uncertainties surrounding the success of these projects. While capacity is often a primary consideration when evaluating Gigafactory investments, other critical factors must also be taken into account. These include geographical location, political considerations, the participation of key market players, and the specific technological configurations employed. In essence, these factors may ultimately exert a more significant influence on the prospects of success within the industry than sheer production capacity.
Existing Battery Capacity and Market Share
Existing Battery Capacity and Market Share
The battery production landscape has been significantly influenced by growing demand for electric vehicle (EV) batteries. Notably, Panasonic, a key Tesla supplier, reported a substantial 45% increase in battery sales in 2022.
A handful of Chinese and South Korean manufacturers have become dominant players in global battery production, serving as benchmarks for the emerging Gigafactory sector. Their early entry into the market gave them an advantage, securing access to critical raw materials, showcasing strong manufacturing capabilities, and establishing vital investment relationships.
Most major players among the top 10 EV battery producers are actively engaged in the rapidly evolving Gigafactory landscape. For instance, CATL, the largest battery producer, initiated Gigafactory plans in Germany, with intentions for expansion. Additionally, entities like SK On, LG Energy, Samsung, and General Motors (GM) have announced strategic joint ventures for Gigafactory projects.
The demand for electric vehicles has led established manufacturers to focus on localizing production capacity, a trend expected to continue. This suggests additional production facilities will likely be located near major demand centres. Many industry leaders have adopted the concept of massive gigawatt-scale factories. For instance, CATL’s battery facility in Germany began with an impressive 8 gigawatt-hours (GWh) production capacity in December 2022, with plans to scale up to 14GWh.
Furthermore, these established manufacturers have pursued vertical integration within their business models, a trend also seen in upcoming Gigafactory projects. Leading global battery manufacturers, such as BYD and Great Wall, have expanded their presence across the entire value chain, enhancing their competitive positions.
Electric Vehicle Battery Producers’ Market Share (2022)
Electric Vehicle Battery Producers’ Market Share (2022)

Capacity Under Development
Capacity Under Development
The Gigafactory landscape has witnessed remarkable growth since 2015 when there were only three projects in development, according to Benchmark Minerals. Fast forward to the 2019, and we find ourselves with a Gigafactory pipeline of 102 projects which has more than tripled to date, now encompassing 363 projects. The driving force behind this expansion is the burgeoning electric vehicle (EV)
industry, which demands localized and cost-effective battery production. Furthermore, policy-driven incentives have amplified investment commitments in two primary regions: North America and Europe. The introduction of the United States Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) in August 2022 not only incentivized domestic production in the US but also incited a European policy race to attract competitive investments.
Number of Global Gigafactory Projects Announced and Under Development
Number of Global Gigafactory Projects Announced and Under Development

Relative Share of Countries in Upcoming Battery Production
Relative Share of Countries in Upcoming Battery Production

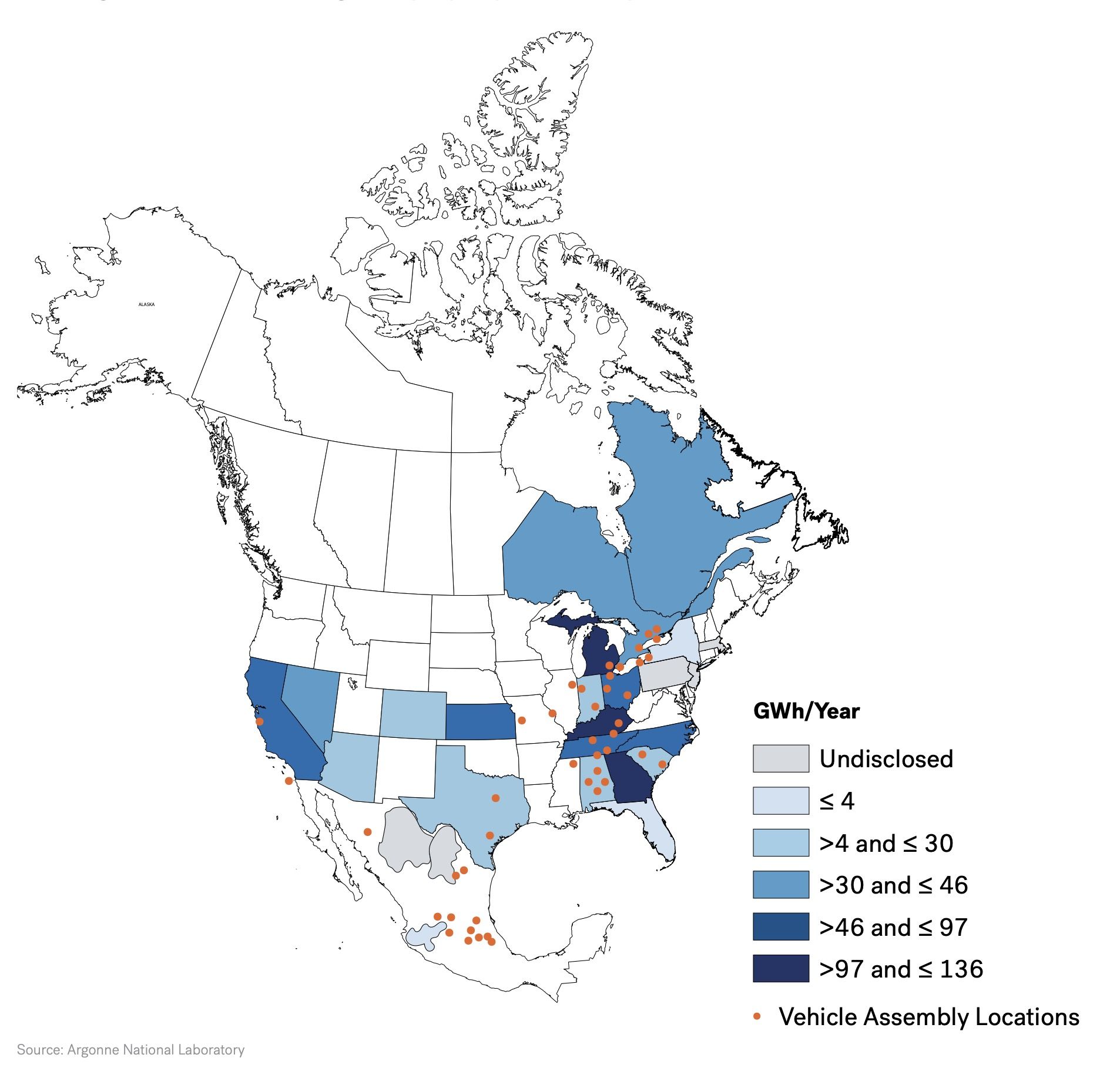
Looking ahead to 2030, it is anticipated that Gigafactories in North America will boast a combined pipeline capacity of 1 terawatt-hour (TWh), spanning across the United States, Canada, and Mexico. Major corporations such as Ford Motors, Ultium, and Hyundai are making substantial investments to bolster capacity in the US. For example, Ford is actively establishing nearly 130 GWh of capacity across three production units, with plans for commissioning within the next 6-7 years. Ultium, a joint venture between General Motors and LG Energy Solutions, along with Tesla, have also announced plans to scale up their manufacturing capacity to 100 GWh each. The emergence of “battery belt” clusters in select US states, including Tennessee, Michigan, Georgia, Arizona, and South Carolina, has been driven by attractive incentives and support measures. Interestingly, these locations often coincide with existing conventional vehicle assembly units, facilitating synergies for developers.
Major Upcoming Gigafactories in the US
Major Upcoming Gigafactories in the US

In Canada, the Gigafactory pipeline has indirectly benefited from the IRA, which spurred increased battery demand from North America and influenced changes in local policy. The Canadian government has adjusted its policies to stay competitive with the US IRA subsidy support. As a result, in April 2023, Volkswagen-led PowerCo committed to investing
7 billion CAD in a 90 GWh Gigafactory to be based in Ontario. Mexico has also gained prominence for US automakers’ electric vehicle manufacturing due to its proximity to the US and the advantages of a free trade agreement. Tesla, for instance, has announced plans for a proposed Gigafactory project in Mexico.
Gigafactory Investments in Canada (Indicative)
Gigafactory Investments in Canada (Indicative)

Announced Capacity for Gigafactory in North America
Announced Capacity for Gigafactory in North America

Clustering of the North American Gigafactory Capacity under Development
Clustering of the North American Gigafactory Capacity under Development
In Europe, the Gigafactory sector has recently shown positive momentum, boasting a pipeline capacity of 1.3 TWh. Germany leads the European Gigafactory project pipeline with an estimated capacity of approximately 365 GWh, followed by Italy and France with roughly 160 GWh each. Legacy automakers like Volvo and Volkswagen (VW) are driving this pipeline, accompanied by the entry of startups and technology providers. Similar to the US, European development plans are partly motivated by the desire to reduce dependence
on Chinese supply chains. However, potential European investors and project developers have remained cautious as policy dynamics continue to evolve. The IRA’s generous incentives have prompted European policymakers to become more assertive in incentivizing Gigafactory investments. The French government, for example, has secured Gigafactory investments through incentive packages and deal sweeteners, although these subsidies await review by the European Commission.
Europe’s Major Tracked Gigafactory Projects under Development
Europe’s Major Tracked Gigafactory Projects under Development

A Regional View of the Planned European Gigafactory Capacity (GWh)
A Regional View of the Planned European Gigafactory Capacity (GWh)

Despite the rapid growth in the global Gigafactory pipeline, several challenges and uncertainties persist, including financial constraints, raw material access, and offtake security. In the US, the UK-based company Britishvolt faced difficulties in executing its planned Canadian Gigafactory, citing challenges in securing finance, among other issues. Similarly, the Ultium joint venture between General Motors and LG Energy decided to pause its plans to develop a fourth Gigafactory project. In Europe, leading companies such as Northvolt, Polestar, and Iberdrola have hinted at potential relocations of their planned facilities. A study by Transport and Environment in February 2023 estimated that one-fifth of the announced Gigafactory
capacity in Europe faces a high risk of delay, downsizing, or cancellation. Addressing these challenges may necessitate a comprehensive region-wide policy shift involving increased financial support for such projects to counteract the influence of competitive subsidies.
In conclusion, the Gigafactory pipeline has experienced rapid expansion due to the surging global demand for EVs and supportive policy changes in Europe and the US. However, investor caution persists, and the landscape remains dynamic as countries engage in a competitive policy race to attract Gigafactory developments.
Evolving Technology Choices
Evolving Technology Choices
The trend of shifting battery chemistry away from lithium- ion production is informative of the growing landscape of upcoming Gigafactories. By the end of 2022, Lithium Nickel Manganese Cobalt Oxide (NMC ) stood as the dominant choice of battery chemistry, followed by Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP) and Nickel Cobalt Aluminium Oxide (NCA). For many battery producers with Gigafactories under development, the choice of battery chemistry is critical, as it involves commitment to a single technology and chemistry for a minimum of 10 years. Due to the evolving nature of battery technology, the Lithium- Ion production pipeline may not accurately represent the future battery production trends.
In March 2023, the company EnerVenue adopted a non- Lithium technology option to set up a Gigafactory in Kentucky, US. The company set up a 1GWh battery production unit for metal-hydrogen batteries. It involves the use of metal hydrides as cathode and anode and hydrogen gas as electrolyte. The first phase of this plant, once stabilized, will make way for expansion to a total 20GWh worth of capacity. The battery process is still being perfected for critical factors like energy density and infrastructure.
The majority of novel battery chemistry technology options are currently awaiting commercial success. An exception to this may be sodium-ion battery technology. The abundant availability of Sodium has increased its cost-effectiveness. This, combined with a potentially higher battery energy density than lithium-ion batteries make for an attractive proposition. A mass scale of production process appears to be gradually taking root, led by the Chinese manufacturers.
Globally, about 20 sodium-ion battery factories are in the planning/development stages (as of April 2023). Chinese companies, with 16 such factories in process, are ahead of the curve in commercializing sodium-ion for electric vehicle deployment.
The application of sodium-ion batteries fit better for grid- scale energy storage segment because they require more space than lithium-ion batteries. So, even as the fine-tuning for automotive use progresses, the demand from utilities and renewable-storage projects presents a significant opportunity. There are other unexplored areas, such as the emission-free aviation (signified in United Airlines’ stake in Natron Energy) that could potentially widen the scope of Sodium-ion batteries.
Trend in Electric Vehicle Battery Chemistry Distribution
Trend in Electric Vehicle Battery Chemistry Distribution

Major Instances of Sodium-Ion Battery Production and Commercialization
Major Instances of Sodium-Ion Battery Production and Commercialization
